Lot Codes vs. Other Codes: Similarities and Differences
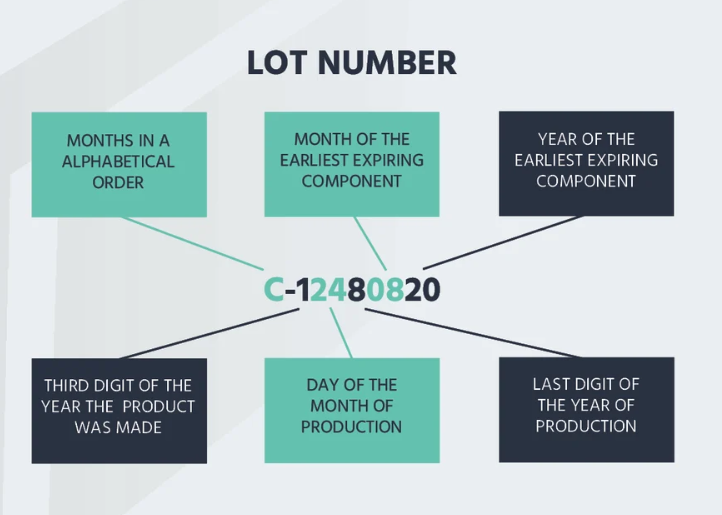
Lot code is a commonly used code for product tracking and management. It identifies products made under the same conditions and usually includes production date, factory, or batch number.
There are many benefits of using lot codes:
- Improved traceability
- Quality control
- Regulatory compliance
For manufacturers, lot codes also help reduce waste and keep supply chains efficient. Understanding lot codes and how they differ from other product codes can enhance overall product management practices.
Other Product Codes
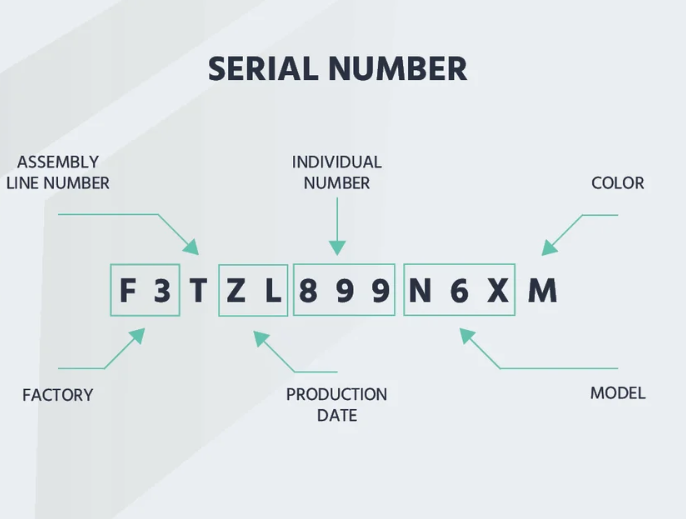
Serial Number
A serial number is a unique alphanumeric code assigned to an individual product or component, distinguishing it from all others of the same model or batch. A serial number can include the production date, batch code, production line, or product variant details, which enable precise product identification, allowing manufacturers and consumers to track production history, verify authenticity, and manage warranty or repair records.
Benefits:
- Enables efficient product tracking and traceability
- Helps prevent counterfeiting and ensures authenticity
- Simplifies warranty claims and service management
- Assists in identifying defective batches for recalls
- Supports data collection and performance analysis
Barcodes (UPC/EAN/GTIN)
Barcodes such as UPC, EAN, or GTIN are machine-readable codes used to identify products globally. Each barcode holds essential data such as product ID, manufacturer, and packaging details, ensuring accuracy in logistics and retail systems. They simplify product tracking, pricing, and inventory management throughout the supply chain.
Benefits:
- Improve inventory accuracy and reduce human error
- Speed up checkout and warehouse operations
- Enable real-time tracking across the supply chain
- Simplify product identification and data management
- Support global trade and standardized product labeling
- Enhance traceability for recalls and quality control
QR Codes
A QR (Quick Response) code is a two-dimensional barcode that stores information in both vertical and horizontal directions, allowing for fast digital scanning. A QR code may include URLs, product specifications, manufacturing information, or batch tracking data. They help to connect physical products to digital data, enabling users to access websites, manuals, promotions, or traceability details with a simple scan.
Benefits:
- Provides instant access to online information
- Enhances product transparency and consumer engagement
- Supports inventory tracking and digital marketing
- Can store more data than traditional barcodes
- Easily scannable by smartphones and industrial scanners

SKU
An SKU is a unique identifier used by retailers and manufacturers to track individual products within inventory systems. SKUs typically encodes details such as product type, size, color, model, and supplier information. They help businesses manage stock efficiently, monitor sales performance, and simplify reordering or product differentiation.
Benefits:
- Improves inventory organization and control
- Simplifies sales tracking and reporting
- Enhances accuracy in warehouse management
- Helps identify best-selling or low-stock items
- Supports efficient logistics and replenishment planning
Similarities and Core Functions
Shared Objectives
Lot codes, serial numbers, barcodes, QR codes, and SKUs all help businesses manage products better. They share common goals. First, they make product identification simple. Each item or batch can be tracked clearly. This helps with inventory management. Businesses can see what is in stock and where it is.
They also support customer service and returns. Codes make it easy to check purchase history, handle warranty claims, and process returns. In regulated industries, these codes are often required by law. They help meet safety and compliance rules.
Overall, using these codes improves efficiency, reduces errors, and ensures products are safe, traceable, and well-managed.
Traceability
Lot codes and other product codes help track products. They show where and when a product was made. If a problem occurs, companies can quickly find the affected items. This makes recalls faster and keeps customers safe.
Traceability also helps control quality. It shows which batch a product comes from. Companies can find problems in production or supply chains. Many industries use traceability. This includes food, electronics, vaccines, and clothing. Lot codes, serial numbers, QR codes, and SKUs make products safe and easy to manage. Handheld printers can print clear codes on products for easy tracking.
Key Differences in Purpose and Application
Focus of Traceability
Each code plays a slightly different role in terms of traceability:
- Serial Numbers: Track individual items. Show full product history. Help verify authenticity, and support warranty or repair management.
- Barcodes: Identify products and manage stock efficiently. Enable fast scanning, accurate inventory, and smooth supply chain operations.
- QR Codes: Store extra information such as links, product details, or batch data. Connect products to digital content and support traceability.
- SKU: Track product variations like size, color, or model within inventory. Simplify stock management, sales monitoring, and warehouse organization.
Necessity by Industry
Codes and batch numbers are crucial for every industry. Using the right code keeps products safe, organized, and compliant.
- Food & Medicine: Lot codes needed for safety and recalls.
- Electronics & High-Value Items: Serial numbers prevent fraud and help with warranties.
- Retail & Online Stores: SKUs and barcodes track stock and speed up checkout.
- Consumer Goods: QR codes link products to online info and improve traceability.
Application Cases
Lot Code Use Cases
Lot codes are used in food, medicine, and other products that need careful tracking. They help trace production batches, find problems, and manage recalls fast.
- Food Recalls: The FDA uses lot codes to find contaminated food. Recent produce and infant formula recalls used lot codes to find affected batches quickly. This removed unsafe products and kept people safe.
- Agriculture: Farmers and suppliers record harvest dates and origins using lot codes. If spoilage happens, they can trace the affected lot to the exact farm.
- Pharmaceuticals: Lot codes on medicine packages track production. They help isolate defective or expired batches before reaching patients.
- Manufacturing: Factories link raw materials to finished products with lot codes. This gives full visibility and faster action on quality issues.
Lot codes improve traceability, shorten recall times, and support safety rules.
Other Code Use Cases
Other codes like serial numbers, barcodes, QR codes, and SKUs are used to track individual products, store information, or manage inventory.
- Electronics: Serial numbers are used to manage warranties and repairs. Each device can be tracked from factory to customer.
- Healthcare: Batch numbers and barcodes on medical devices and vaccines improve safety by tracking each unit to hospitals and clinics.
- Luxury Goods: Serial numbers and QR codes help prevent counterfeiting. Customers can scan codes to verify authenticity and access product information.
- Retail & Logistics: SKUs, barcodes, and QR codes are used to track sales, organize warehouses, and update inventory digitally, reducing errors and saving time.
These codes make product tracking simple, support service and warranty, and protect consumers and brands.
How to Print These Codes
There are several types of coding and marking equipment that can be used to print different codes on products or packaging. Among them, handheld inkjet printers, laser coders, and thermal transfer printers are the most common solutions. Each technology offers distinct advantages in terms of material compatibility, marking quality, and production needs.
Handheld Inkjet Printers
Handheld inkjet printers - one of the best solutions for printing these codes. They use cartridge-based ink systems to print directly on various surfaces, including paper, plastic, metal, and wood. To print codes, users simply design the content, such as barcodes, QR codes, batch numbers, or logos, through the printer's built-in touchscreen, or transfer data via USB drive, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth (depending on each printer's availability), then move the device across the target surface. The printer automatically sprays ink in the set pattern, creating clear and durable marks. This portable solution is ideal for small batches, on-site labeling, and flexible production needs.
Laser Coders
Laser coders mark information such as batch numbers, expiration dates, and barcodes directly onto product surfaces using a focused laser beam. The process involves no ink or consumables. To print codes, the product passes under the laser marking head while the beam is directed and controlled by software. Operators can set up the code design, adjust marking speed and contrast, and choose the right laser type such as CO₂, fiber, or UV, depending on the material. This ensures precise, permanent, and maintenance-free coding suitable for high-speed production lines.
Thermal / Thermal Transfer Printers
Thermal transfer printers use heat to transfer ink from a ribbon onto labels, films, or flexible packaging. During printing, the printhead heats specific areas of the ribbon, causing the ink to melt and adhere to the surface in the desired pattern. To print codes, users can upload data via USB drive, network connection, or integrated software, then select print settings such as speed and temperature. This technology delivers sharp, smudge-resistant prints, making it ideal for date codes, barcodes, and product identification on packaging materials.
In Conclusion
Lot coding is a key tool for tracking and managing products. It helps businesses know where items come from, when they were made, and which batch they belong to. Along with serial numbers, barcodes, QR codes, and SKUs, these codes improves inventory management, supports recalls, and ensures product safety. Using the right printing methods, such as handheld inkjet printers, laser coders, or thermal transfer printers, makes coding and marking clear, durable, and easy to read. Implementing lot coding effectively reduces errors, saves time, and keeps products organized, safe, and fully traceable.
Ask Question
No questions and answers